
Writing About AI
Uvation
Reen Singh is an engineer and a technologist with a diverse background spanning software, hardware, aerospace, defense, and cybersecurity. As CTO at Uvation, he leverages his extensive experience to lead the company’s technological innovation and development.

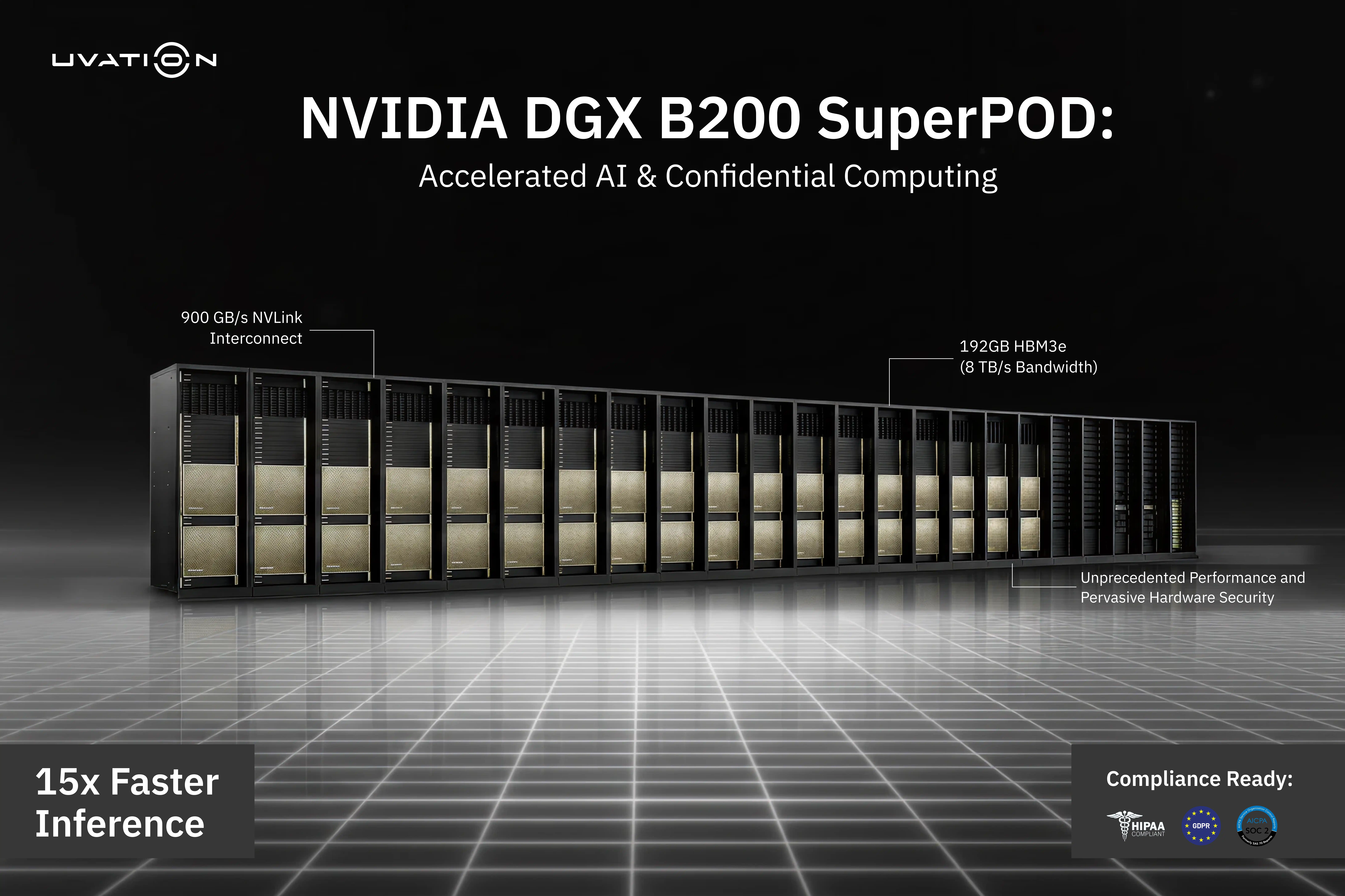
The NVIDIA DGX B200 system is the next generation of accelerated computing infrastructure, purpose-built for the most demanding AI and High-Performance Computing (HPC) workloads. It leverages the NVIDIA Blackwell Architecture to function as a critical component within industrial-scale supercomputing systems, known as DGX SuperPODs, which are engineered specifically to handle tasks like training trillion-parameter models. The architectural focus is on significantly boosting memory capabilities and integrating pervasive, hardware-backed security.
The Blackwell architecture introduces major advancements, particularly in the GPU memory subsystem, which helps overcome data bottlenecks in large-scale AI. The B200 GPU features 192GB HBM3e memory, representing a 76% increase compared to the H100 (80GB HBM3). Furthermore, it offers a massive memory bandwidth of 8 TB/s, which is a 1.4X increase over the H200 (4.8 TB/s). This results in significantly accelerated performance, offering 15x faster inference compared to the H100 for Large Language Models (LLMs).
The substantial increase in memory (192GB HBM3e) and bandwidth (8 TB/s) is essential because it allows extremely large models, such as Llama 4 Maverick 400B or Mixtral-8×22B, to run at full precision on a single node. This capability simplifies the overall architecture by eliminating the need for complex tensor-parallel splitting of the model across multiple GPUs. A standard DGX B200 system is designed to house eight NVIDIA B200 Tensor Core GPUs.
Internally, the eight GPUs within a standard DGX B200 system utilize fourth-generation NVIDIA NVLink to deliver 900 GB/s of GPU-to-GPU bandwidth, ensuring seamless communication within the node. For external connectivity, the systems are equipped with NVIDIA ConnectX-7 network cards, supporting speeds up to 400Gbps for both InfiniBand and Ethernet.
The B200 architecture integrates Confidential Computing (CC), positioning it as a highly secure platform engineered to provide “unruggable” AI by incorporating hardware security across the entire computational lifecycle. Security is achieved via Full-Stack Protection, combining a CPU-based Trusted Execution Environment (TEE), such as Intel TDX, with the GPU’s native NVIDIA Confidential Computing features. This dual-layer approach isolates the entire virtual machine (VM) from the host OS and hypervisor, preventing unauthorized memory access.
When the system operates in NVIDIA Confidential Computing (CC) mode, the Blackwell GPU encrypts all data in GPU memory, protecting model weights, training data, and inference results during the computation. Furthermore, in the multiple GPU pass-through mode, the NVLink pathway is also encrypted, ensuring secure data traffic between GPUs. Blackwell also introduces support for TDISP and IDE, which facilitates direct communication with inline encryption between the GPU and the Confidential Virtual Machine (CVM), eliminating the latency associated with previous software-based bounce buffers.
The system supports Dual Remote Attestation from both Intel TDX and NVIDIA, which allows users or relying parties to cryptographically verify the integrity of the execution environment. This process confirms that the workload is running on genuine hardware with verified code, establishing a crucial chain of trust. The system also incorporates security features like Secure Flash and firmware encryption using the AES-CBC algorithm (128 bits or higher key strength) to prevent the installation of unsigned or unverified firmware images.
The hardware-backed security measures provided by the DGX B200 are crucial for streamlining enterprise AI deployment in highly regulated sectors. These features help organizations meet strict regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 requirements. The architecture is specifically suitable for sensitive AI training and deployment on data (e.g., healthcare, financial, or legal data) where the information must not leave the Trusted Execution Environment (TEE). For computationally intensive workloads like Large Language Models (LLMs), the performance overhead introduced by running in TEE mode is designed to be minimal, approaching near-native speeds.
We are writing frequenly. Don’t miss that.

Unregistered User
It seems you are not registered on this platform. Sign up in order to submit a comment.
Sign up now